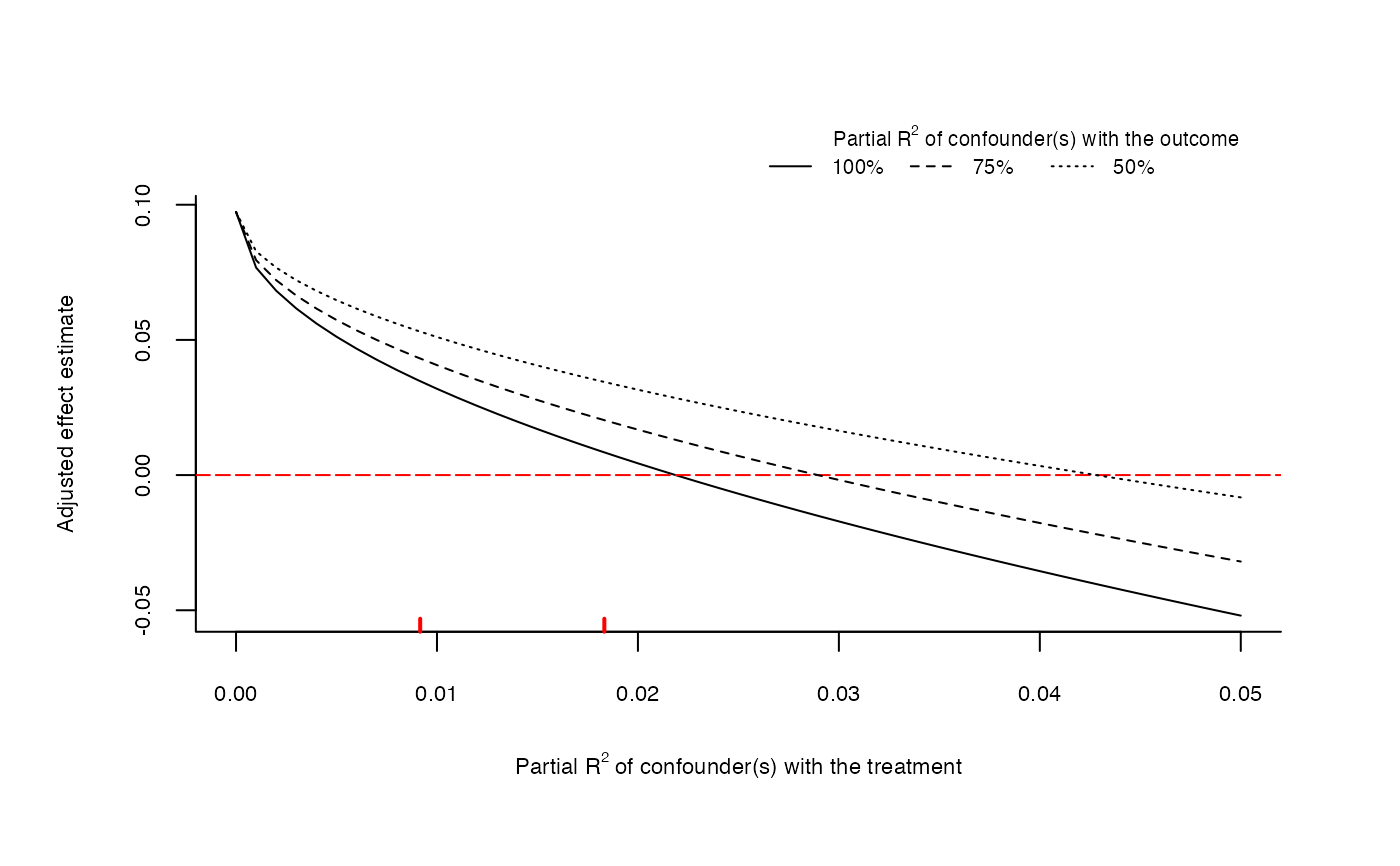
Extreme scenario plots of omitted variable bias for sensitivity analysis. The main inputs are an lm model, the treatment variable
and the covariates used for benchmarking the strength of unobserved confounding.
The horizontal axis shows the partial R2 of the unobserved confounder(s) with the treatment. The vertical axis shows the adjusted treatment effect estimate.
The partial R2 of the confounder with the outcome is represented by different curves for each scenario, as given by the parameter r2yz.dx.
The red marks on horizontal axis are bounds on the partial R2 of the unobserved confounder kd times as strong as the covariates used for benchmarking.
The dotted red line represent the threshold for the effect estimate deemed to be problematic (for instance, zero).
See Cinelli and Hazlett (2020) for details.
ovb_extreme_plot(model, ...)
# S3 method for lm
ovb_extreme_plot(
model,
treatment,
benchmark_covariates = NULL,
kd = 1,
r2yz.dx = c(1, 0.75, 0.5),
r2dz.x = NULL,
reduce = TRUE,
threshold = 0,
lim = min(c(r2dz.x + 0.1, 0.5)),
legend = TRUE,
cex.legend = 0.65,
legend.bty = "n",
...
)
# S3 method for fixest
ovb_extreme_plot(
model,
treatment,
benchmark_covariates = NULL,
kd = 1,
r2yz.dx = c(1, 0.75, 0.5),
r2dz.x = NULL,
reduce = TRUE,
threshold = 0,
lim = min(c(r2dz.x + 0.1, 0.5)),
legend = TRUE,
cex.legend = 0.65,
legend.bty = "n",
...
)
# S3 method for formula
ovb_extreme_plot(
formula,
method = c("lm", "feols"),
vcov = "iid",
data,
treatment,
benchmark_covariates = NULL,
kd = 1,
r2yz.dx = c(1, 0.75, 0.5),
r2dz.x = NULL,
reduce = TRUE,
threshold = 0,
lim = min(c(r2dz.x + 0.1, 0.5)),
legend = TRUE,
cex.legend = 0.65,
legend.bty = "n",
...
)
# S3 method for numeric
ovb_extreme_plot(
estimate,
se,
dof,
r2dz.x = NULL,
r2yz.dx = c(1, 0.75, 0.5),
reduce = TRUE,
threshold = 0,
lim = min(c(r2dz.x + 0.1, 0.5)),
legend = TRUE,
legend.title = NULL,
cex.legend = 0.65,
legend.bty = "n",
xlab = NULL,
ylab = NULL,
cex.lab = 0.7,
cex.axis = 0.7,
list.par = list(oma = c(1, 1, 1, 1)),
...
)Arguments
- model
An
fixestobject with the outcome regression.- ...
arguments passed to other methods. First argument should either be an
lmmodel with the outcome regression, aformuladescribing the model along with thedata.framecontaining the variables of the model, or a numeric vector with the coefficient estimate.- treatment
A character vector with the name of the treatment variable of the model.
- benchmark_covariates
The user has two options: (i) character vector of the names of covariates that will be used to bound the plausible strength of the unobserved confounders. Each variable will be considered separately; (ii) a named list with character vector names of covariates that will be used, as a group, to bound the plausible strength of the unobserved confounders. The names of the list will be used for the benchmark labels. Note: for factor variables with more than two levels, you need to provide the name of each level as encoded in the
fixestmodel (the columns ofmodel.matrix).- kd
numeric vector. Parameterizes how many times stronger the confounder is related to the treatment in comparison to the observed benchmark covariate. Default value is
1(confounder is as strong as benchmark covariate).- r2yz.dx
Hypothetical partial R2 of unobserved confounder Z with outcome Y, given covariates X and treatment D.
- r2dz.x
Hypothetical partial R2 of unobserved confounder Z with treatment D, given covariates X.
- reduce
Should the bias adjustment reduce or increase the absolute value of the estimated coefficient? Default is
TRUE.- threshold
estimate threshold.
- lim
sets limit for x-axis. If `NULL`, limits are computed automatically.
- legend
should legend be plotted? Default is
TRUE.- cex.legend
size of the text for the legend.
- legend.bty
legend box. See
btyargument of par.- formula
an object of the class
formula: a symbolic description of the model to be fitted.- method
the default is
lm. This argument can be changed to estimate the model usingfeols. In this case the formula needs to be written so it can be estimated withfeolsand the package needs to be installed.- vcov
the variance/covariance used in the estimation when using
feols. Seevcov.fixestfor more details. Defaults to "iid".- data
data needed only when you pass a formula as first parameter. An object of the class
data.framecontaining the variables used in the analysis.- estimate
Coefficient estimate.
- se
Standard error of the coefficient estimate.
- dof
Residual degrees of freedom of the regression.
- legend.title
the legend title. If
NULL, then default legend is used.- xlab
label of x axis. If `NULL`, default label is used.
- ylab
label of y axis. If `NULL`, default label is used.
- cex.lab
The magnification to be used for x and y labels relative to the current setting of cex.
- cex.axis
The magnification to be used for axis annotation relative to the current setting of cex.
- list.par
arguments to be passed to
par. It needs to be a named list.
Value
The function returns invisibly the data used for the extreme plot.
References
Cinelli, C. and Hazlett, C. (2020), "Making Sense of Sensitivity: Extending Omitted Variable Bias." Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B (Statistical Methodology).
Examples
# runs regression model
model <- lm(peacefactor ~ directlyharmed + age + farmer_dar + herder_dar +
pastvoted + hhsize_darfur + female + village,
data = darfur)
# extreme scenarios plot
ovb_extreme_plot(model, treatment = "directlyharmed",
benchmark_covariates = "female",
kd = 1:2,
lim = 0.05)